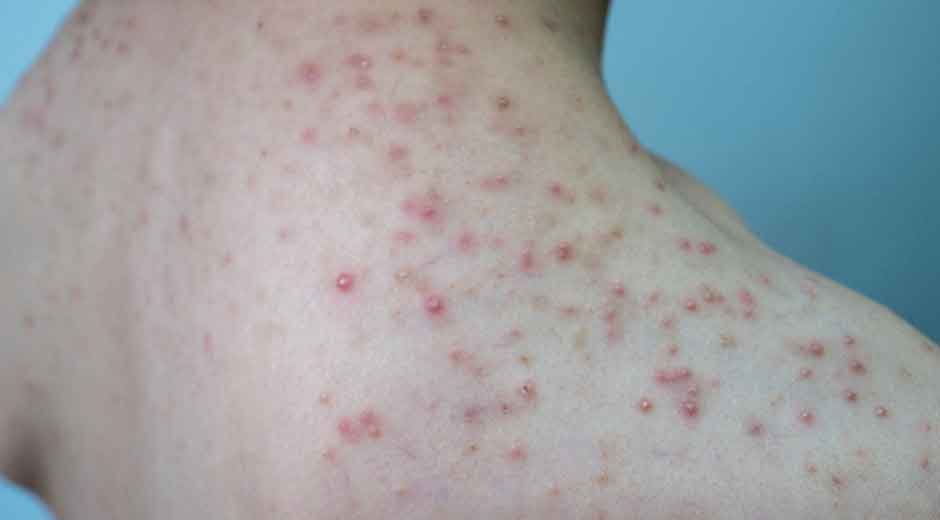
Fungal acne is a frequently overlooked but increasingly common skin condition that can affect the back, chest, shoulders, and face. Unlike conventional acne, fungal acne is caused by an overgrowth of yeast (Malassezia) in the hair follicles. If left untreated, it can persist for months and even lead to post-acne scarring, which makes professional guidance essential.
For patients dealing with widespread or persistent fungal acne, professional intervention can make a significant difference. Treatments such as acne scarring treatment Singapore can not only manage active breakouts but also address post-inflammatory marks and prevent long-term skin damage.
Understanding how to manage fungal acne effectively is critical, especially in humid climates like Singapore where heat and moisture accelerate yeast growth. In this guide, we’ll provide an authoritative overview of how to treat fungal acne across multiple body areas, and how to prevent recurrence.
Table of Contents
ToggleRecognizing Fungal Acne
Unlike typical acne caused by bacteria or clogged pores, fungal acne presents with distinct characteristics:
- Small, uniform bumps: Papules or pustules that appear similar in size.
- Pruritus (itchiness): Often accompanied by mild irritation or burning sensation.
- Commonly affected areas: Upper back, chest, shoulders, neck, and sometimes the face.
- Resistance to traditional acne treatments: Topical antibiotics or benzoyl peroxide often have little effect.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial because treating fungal acne like conventional acne is often ineffective and can prolong symptoms.
Why Fungal Acne Occurs Across Multiple Body Areas
Fungal acne thrives in environments with:
- Heat and moisture: Sweat and humidity create ideal conditions for yeast overgrowth.
- Occlusion: Tight clothing, straps, and gear trap moisture against the skin.
- Sebum-rich areas: The yeast feeds on natural oils produced by the skin.
These factors explain why fungal acne commonly affects not only the face but also the upper body, including the back, chest, and shoulders.
Professional Approach to Treatment
Effective management of fungal acne requires a combination of antifungal therapies, skincare adjustments, and lifestyle measures. Innovations in teledermatology, such as hellowisp, have made professional guidance more accessible, allowing patients to consult specialists even for widespread fungal acne.
1. Antifungal Cleansers and Body Washes
Topical antifungal washes form the cornerstone of fungal acne treatment. Ingredients such as ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or zinc pyrithione can reduce yeast overgrowth.
Recommended use:
- Apply to affected areas 2–3 times per week during flare-ups.
- Leave on for 3–5 minutes before rinsing.
- Reduce to 1–2 times per week for maintenance once improvement is observed.
2. Topical Antifungal Treatments
For persistent or localized lesions, dermatologists may prescribe antifungal creams or lotions. These are typically applied to affected areas twice daily until resolution and may be tapered afterward.
3. Oral Antifungal Therapy
In severe or widespread cases, systemic treatment may be necessary. Oral antifungal medications can be highly effective but require medical supervision due to potential side effects and liver considerations.
4. Skincare and Lifestyle Adjustments
Professional management extends beyond medications:
- Switch to lightweight, non-comedogenic skincare: Avoid heavy oils or creams that feed yeast.
- Wear breathable clothing: Cotton and moisture-wicking fabrics reduce occlusion.
- Shower promptly after sweating: Reduces yeast proliferation on the skin.
- Maintain clean linens and workout gear: Prevents reinfection from residual oils or yeast.
5. Professional Assessment and Scarring Treatment
For patients with persistent fungal acne or post-inflammatory marks, consulting a specialist is advised. Early intervention can prevent long-term pigmentation or scarring. For example, professional acne scarring treatment in Singapore is an effective way to restore skin clarity while preventing recurrence.
Expected Timeline for Improvement
Under proper guidance, patients can expect:
- 2–4 weeks: Noticeable reduction in itchiness and new breakouts.
- 4–6 weeks: Significant improvement in lesion appearance.
- 6–8 weeks: Near-complete resolution when treatment and lifestyle adjustments are consistently applied.
It is important to maintain preventive measures to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Why Standard Acne Treatments Often Fail
Conventional acne products target bacteria or clogged pores rather than yeast. This is why treatments like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and oral antibiotics often show minimal results in fungal acne. Heavy creams or oily moisturizers can exacerbate the condition by providing additional nutrients for yeast growth.
Prevention and Long-Term Management
Professional advice emphasizes consistent hygiene and preventive strategies:
- Maintain routine antifungal wash usage even after clearing.
- Wear breathable clothing to reduce moisture accumulation.
- Promptly shower after sweating to limit yeast proliferation.
- Use lightweight, non-comedogenic skincare for all affected areas.
- Regularly clean linens, towels, and workout gear.
Adhering to these steps reduces recurrence and ensures long-term skin health.
When to Consult a Dermatologist
Seek professional guidance if:
- Fungal acne persists beyond several weeks despite proper care.
- It affects multiple areas of the body and interferes with daily life.
- Post-inflammatory pigmentation or scarring begins to appear.
- Over-the-counter treatments fail to provide improvement.
Early consultation ensures targeted therapy, reduces the risk of scarring, and provides access to professional follow-up care.
Conclusion: A Strategic Approach to Fungal Acne
Fungal acne requires a professional, evidence-based approach. Combining antifungal therapy, lifestyle modification, and consistent skincare management allows for effective resolution.
In humid climates, especially, prevention through proactive measures is just as important as treatment. Maintaining routine antifungal care, avoiding triggers, and seeking timely dermatological support ensures long-lasting results.
For those experiencing persistent fungal acne or its aftermath, professional interventions such as acne scarring treatment in Singapore provide expert guidance, restore skin clarity, and prevent recurrence.
Ultimately, fungal acne is highly manageable when addressed with the correct medical strategy — even when it affects multiple areas of the body.